Introduction to CITES and Its Role in Wildlife Trade
When it comes to regulating and monitoring international trade in endangered species, the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) stands out as a vital global agreement. CITES was established in 1975 and currently boasts 183 member countries, making it one of the most significant environmental agreements worldwide.
The Significance of CITES
CITES plays a crucial role in protecting wildlife by ensuring that the international trade of endangered species does not threaten their survival in the wild. It provides a framework for countries to cooperate in implementing strict controls on the exploitation and trade of vulnerable species, thereby safeguarding biodiversity and promoting sustainable use of natural resources.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its importance, CITES faces challenges such as illegal wildlife trafficking, inadequate enforcement in some regions, and the need for improved data collection and reporting. Opportunities lie in enhancing collaboration among member states, leveraging technology for monitoring and enforcement, and increasing public awareness about the significance of combating illegal wildlife trade.
The Future of CITES in Wildlife Trade
Looking ahead, the future of CITES in wildlife trade will likely involve a continued focus on strengthening enforcement mechanisms, enhancing transparency in trade data, and adapting to emerging threats such as online wildlife trafficking. As the entertainment industry increasingly emphasizes sustainability and ethical sourcing practices, CITES will play a crucial role in ensuring that wildlife trade regulations align with these evolving standards.
Analyzing CITES Data: Implications for Wildcats
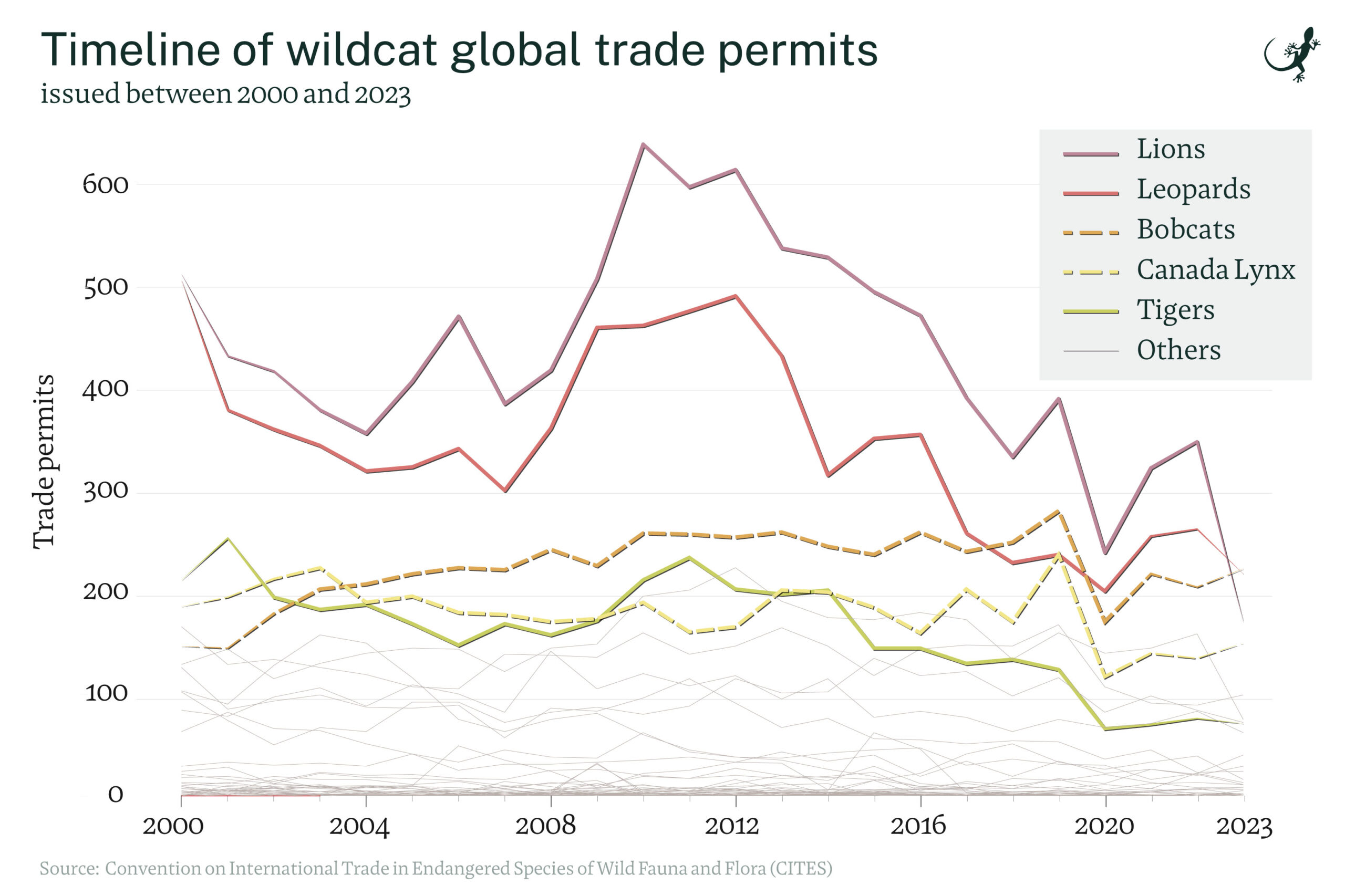
When delving into the analysis of CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) data concerning wildcats, profound insights emerge that carry significant implications for the conservation of these majestic creatures. CITES serves as a crucial regulatory framework aimed at safeguarding endangered species by regulating and monitoring international trade. By scrutinizing the data provided by CITES, conservationists and governmental bodies can paint a vivid picture of the threats faced by wildcats worldwide.
Wildcats, including species like tigers, leopards, and jaguars, are subjected to numerous threats such as habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. The analysis of CITES data reveals the gravity of these challenges, showcasing the urgent need for enhanced conservation efforts to protect these iconic species from the brink of extinction.
Furthermore, the implications derived from CITES data underscore the importance of collaborative global conservation initiatives. International cooperation is imperative in combatting wildlife crimes and ensuring the survival of wildcats. By leveraging the data provided by CITES, stakeholders can strategize and implement comprehensive measures to address the root causes of endangerment faced by wildcats.
In conclusion, the analysis of CITES data plays a pivotal role in shedding light on the plight of wildcats and guiding conservation actions. It highlights the pressing need for unified efforts to safeguard these magnificent creatures and preserve biodiversity for future generations.
Legal Framework Governing Wildcat Trade
When delving into the world of wildcat trade, understanding the legal framework is crucial. Regulations vary widely across regions, encompassing laws related to wildlife protection, trafficking, and trade. To navigate this complex landscape successfully and ethically, individuals and organizations involved in wildcat trade must stay well-informed about local and international legislation.
Challenges and Opportunities in Regulating Wildcat Trade
Breaking Down the Headlines
Wildcat trade, which involves the illegal trafficking of wild animals and their parts, presents significant challenges for regulators worldwide. The exploitation of endangered species not only threatens biodiversity but also fuels organized crime and poses risks to public health.
The Bigger Picture
Efforts to combat wildcat trade are crucial for preserving ecosystems and protecting endangered species. Tackling this illicit activity requires international cooperation, increased enforcement measures, and public awareness campaigns to curb demand.
What This Means Going Forward
As governments strengthen regulations and enforcement mechanisms, there is an opportunity to disrupt the supply chain of wildcat trade and reduce its impact. Enhancing collaboration between law enforcement agencies, conservation groups, and communities is key to effectively combating this illicit trade and safeguarding wildlife for future generations.