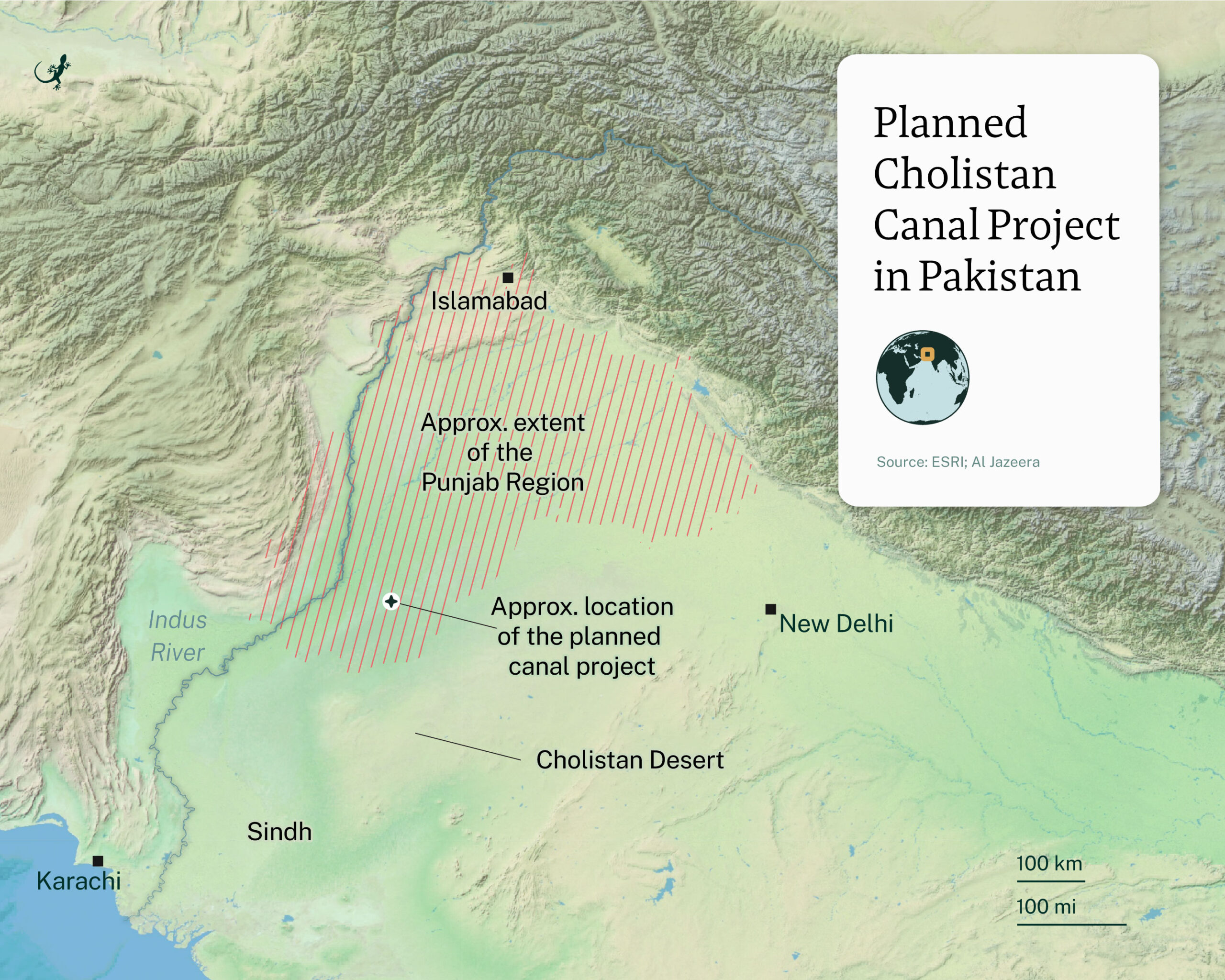
Exploring Pakistan’s Ambitious Desert Irrigation Projects
Pakistan’s ambitious desert irrigation projects represent a significant leap towards sustainable agricultural practices in arid regions. These initiatives aim to harness advanced irrigation technologies to transform vast stretches of desert land into fertile farming areas, thereby enhancing food security and livelihood opportunities.
Innovative Water Management Strategies Driving Success
The success of Pakistan’s desert irrigation projects heavily relies on innovative water management strategies such as drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and canal lining. By utilizing modern irrigation techniques, minimal water is maximally utilized, reducing wastage and ensuring efficient crop cultivation in arid environments. These strategies play a crucial role in mitigating water scarcity challenges and increasing agricultural productivity in the region.
Sustainable Development and Economic Benefits
These irrigation projects not only contribute to sustainable development but also offer significant economic benefits. By converting barren deserts into fertile agricultural lands, Pakistan can boost its agricultural output, reduce dependency on imported food, create employment opportunities, and drive economic growth in rural areas. Moreover, the promotion of crop diversification and adoption of climate-resilient farming practices further enhance the ecological sustainability of these regions.
Paving the Way for Transformative Change
Pakistan’s ambitious desert irrigation projects symbolize a transformative change in the country’s agricultural landscape. Through the integration of modern technologies, sustainable practices, and strategic planning, these projects have the potential to revolutionize farming in arid regions, setting a benchmark for water-efficient agriculture and environmental conservation. As these initiatives unfold, they serve as a beacon of hope for addressing food security challenges and promoting sustainable development in desert areas.
Concerns and Protests from Sindh’s Agricultural Community
Being the backbone of Pakistan’s agrarian economy, Sindh’s agricultural community plays a vital role in ensuring food security and economic stability. However, recent events have sparked concerns and protests within this crucial sector.
Issues such as water scarcity, land grabbing, lack of government support, and fluctuating market prices have been plaguing the farmers in Sindh. The exploitation of small-scale farmers by powerful landlords and the unequal distribution of resources further exacerbate the challenges faced by the agricultural community.
These concerns have led to widespread protests and demonstrations across Sindh, as farmers demand fair treatment, better agricultural policies, and access to essential resources. The protests signify a deep-rooted discontent and highlight the urgent need for structural reforms and policy interventions to safeguard the interests of those working in the agricultural sector.
The plight of Sindh’s agricultural community is an issue of national importance, impacting not only the livelihoods of farmers but also the overall food security and economic prosperity of the country. It is imperative for the authorities to address these concerns promptly and work towards creating a more equitable and sustainable environment for the agricultural workforce in Sindh.
Exploring the Environmental Impacts of Desert Irrigation in Pakistan
Desert irrigation in Pakistan has profound environmental implications that must be carefully considered and managed. While irrigation transforms arid lands into productive areas, it also brings about various environmental challenges.
Water Scarcity
One major concern is the exacerbation of water scarcity. Increased irrigation in deserts can put pressure on already limited water resources, leading to depletion of aquifers and water tables.
Soil Degradation
Intensive irrigation practices can contribute to soil salinization and degradation. Excessive salts from irrigation water can accumulate in the soil over time, rendering it infertile and impacting agricultural productivity.
Biodiversity Loss
The altered landscape due to desert irrigation can disrupt local ecosystems and habitats, leading to biodiversity loss. Native flora and fauna may struggle to survive in these transformed environments.
Energy Consumption
Desert irrigation often requires significant energy inputs, especially in arid regions like Pakistan. Pumping water over long distances and operating irrigation systems demand substantial energy resources, contributing to carbon emissions and air pollution.
Effective Management Solutions
To mitigate these environmental impacts, sustainable irrigation practices such as drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and proper soil management can be implemented. Additionally, promoting water-efficient crops and technologies can help conserve resources while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Future of Farming in Sindh Amid Proposed Irrigation Plans
Breaking Down the Headlines
Proposed irrigation plans in Sindh are sparking discussions on the future of farming in the region. The potential impact of these plans on agricultural productivity, water usage, and the livelihoods of farmers is at the forefront of current debates.
The Bigger Picture
Understanding the future of farming in Sindh requires delving into the historical significance of irrigation systems in the region. Sindh has a long tradition of agriculture dating back centuries, with irrigation serving as a cornerstone of its farming practices. Any proposed changes to irrigation infrastructure have the potential to reshape the agricultural landscape and rural economy of the region.
What This Means Going Forward
The proposed irrigation plans in Sindh will likely have far-reaching consequences for various stakeholders. Farmers will need to adapt to new techniques and water management practices. Agricultural businesses and food supply chains may experience shifts in production and distribution. Additionally, there could be environmental impacts to consider, such as changes in water availability and ecosystem sustainability. Keeping a close eye on the implementation of these plans will be crucial for assessing their actual impact on the future of farming in Sindh.